Smartphone contact tracing
Bluetooth technology, the best ally to detect COVID-19 cases according to a UPV study
[ 10/06/2020 ]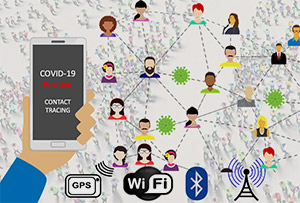
A study carried out by researchers at the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and published in the IEEE Access journal concludes that Bluetooth technology is the best ally to detect possible COVID-19 cases through smartphone contact tracing. The key is the high level of precision, higher than other technologies, such as GPS, cell phone networks and Wi-Fi.
“Tracers have been and are essential to manage the pandemic. Today, the tracing is done by hand and this work is slow and inaccurate. However, as we have seen, technology can be highly useful: contact tracing with smartphones and smartclocks help find out who has been in contact with an infected person, thanks to the use of localization and communication technologies, such as GPS, cell phone networks, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth,” explains Enrique Hernández Orallo, researcher at the Networking Research Group-DISCA of the Universitat Politècnica de València.
In their study, UPV researchers assessed the effectiveness of each one of these technologies. In order to do that, they designed an epidemiological mathematical model which allowed them to study its efficiency and impact—in terms of number of persons that must enter in self-quarantine from the results obtained. “Bluetooth is the most suitable technology because it allows tracers to detect contacts within a range of 2-3 meters. Those contacts are considered by epidemiological models as a contact capable of passing the infection. Therefore, it helps to reduce the number of false contacts, and also allows them to be more efficient when establishing which people must self-quarantine,” explains Enrique Hernández Orallo.
“Extremely useful” in a possible new outbreak
Since the infection rate of COVID is extremely high, the contact tracing technology must be accurate and perform a quick search. However, in order to do it more effectively, a significant percentage of the population must install the contact tracing application on their smart devices.
“These strict requirements make contact tracing based on smartphones quite inefficient to contain the infection propagation during the first outbreak of the virus. However, in the case of a new outbreak of the pandemic, with a percentage of the population immune, or in combination with other less strict measures that reduce the spread of the virus (such as social distancing), contact tracing based on smartphones could be extremely useful, even if only a part of the population—less than 60%—would be willing to use it. In any case, Bluetooth will be the most suitable tool to do the tracing,” concludes Hernández Orallo.
Outstanding news
 ARWU 2023
ARWU 2023
The Shanghai ranking reaffirms the UPV as the best polytechnic in Spain for yet another year
 Science Meets Regions CV 2023
Science Meets Regions CV 2023
The UPV and the Almussafes City Council begin a collaboration in search of solutions to maintain the automobile sector in the Valencia Region
 Scientific reference
Scientific reference
Avelino Corma, Distinguished Research Assistant at the UPV, awarded an Honorary Doctorate by the University of Huelva
 Micronanofabs NTC UPV-PERTE CHIP Conference
Micronanofabs NTC UPV-PERTE CHIP Conference
María Marced, TSMC Europe president: "The sector's future is bright, the market is expected to double by 2030"
 Goya nomination
Goya nomination
Javier Polo, who holds a degree in Audiovisual Communication from the UPV, directs the successful short documentary Una terapia de mierda
 Sant Carles Medal 2023
Sant Carles Medal 2023
The Faculty of Fine Arts of the UPV awards the Sant Carles Medal 2023 to outstanding Valencian art and culture figures